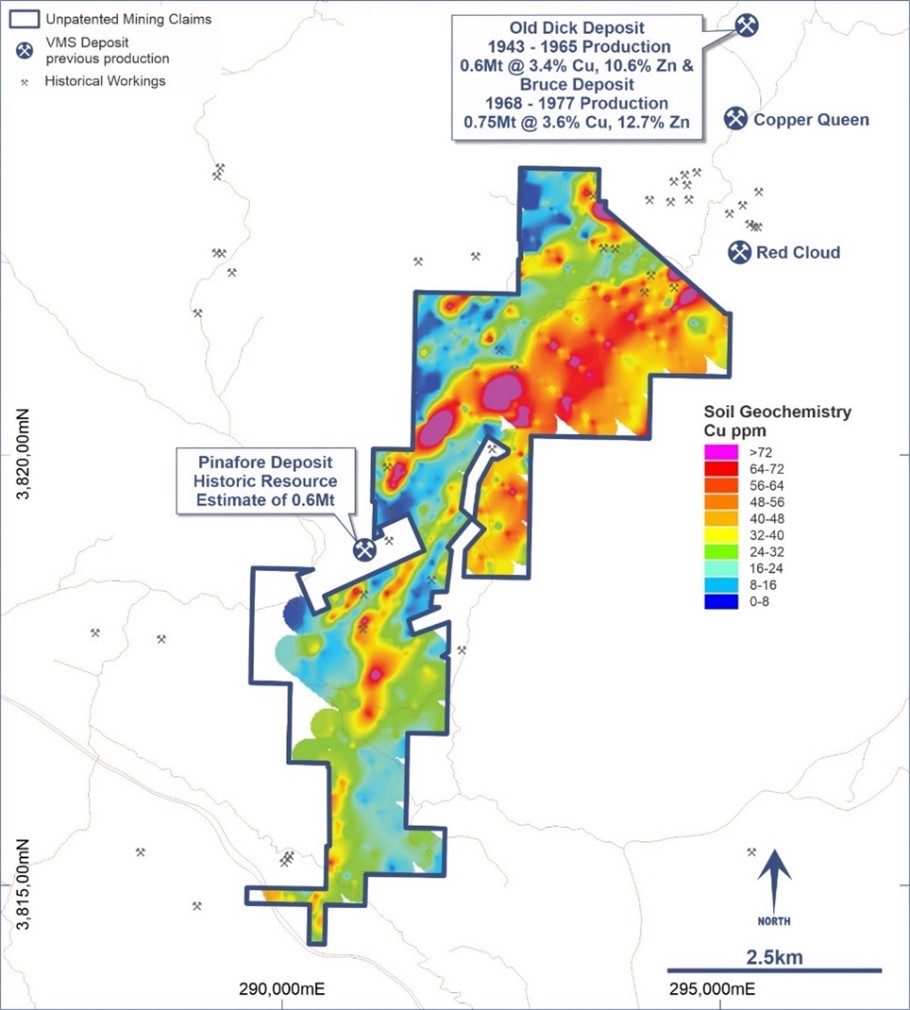
New World has staked a contiguous series of mining claims covering approximately 4,500 acres in an area approximately 75km to the south-east of the Antler Deposit, just south of the Bagdad porphyry copper deposit (the location of the 5th largest copper mine in the US; currently operated by Freeport-McMoRan Inc.). These 100%-owned mining claims comprise the Company’s Javelin VMS Project.
These mining claims cover almost 10km of the strike extensions of the geological sequences that host numerous high-grade volcanogenic massive sulphide (VMS) Cu-Zn-Pb-Ag-Au deposits that are of similar age and style to the Antler Deposit. Notable deposits in the district include:
While reconnaissance exploration has been undertaken previously, including mapping that identified numerous highly anomalous characteristics that could be associated with VMS mineralisation, there are no records of any drilling being undertaken within the boundaries of New World’s current project area.
During H1 2023 New World completed soil sampling over the entire project area. Extensive highly elevated multi-element geochemistry anomalies have been delineated, including strong copper, zinc, lead, silver and gold anomalies.
An Induced Polarisation (“IP”) geophysical survey was subsequently undertaken over the northern portion of the Project area to refine and prioritise targets in advance of the Company’s maiden drilling program. Several compelling IP targets were delineated, comprising:
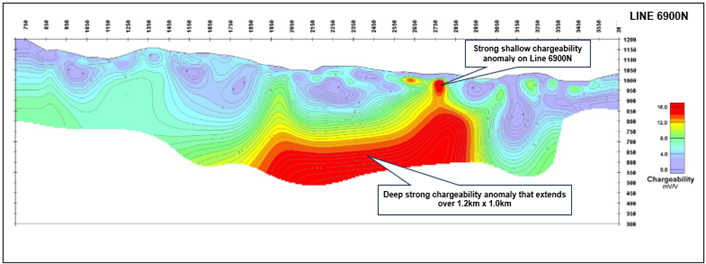
1. A Shallow Chargeability Anomaly on Line 6900N
A strong, shallow, chargeability anomaly delineated around 2750E on the northernmost survey line, Line 6900N. There is a strong but slightly deeper chargeability anomaly centred on 2850E on adjoining line 6700N, which suggests that these two responses may arise from a chargeable source that plunges from north to south.
These anomalies lie in a position in the geological sequence where VMS deposits would be expected to occur and therefore represent compelling exploration targets.
2. A Deeper, Very Strong Chargeability Anomaly Extending Over 1.2km x 1.0km
A very strong, apparently flat-lying chargeability anomaly is evident on the five northernmost survey lines. This anomalism covers an area measuring approximately 1.2km x 1.0km.
Extensive Mineralisation and Alteration
During Q4 2023 extensive alteration and mineralisation has ben found to outcrop immediately above and along strike from these very strong IP anomalies.
A 2km-long corridor that is highly prospective for VMS mineralisation has now been delineated, which includes:
Drilling to Commence in January 2024
The Company has been granted the requisite permit to commence drill testing these targets. A reclamation bond is currently being put in place, following which drilling can commence. A drill rig is being mobilized to the project area in December 2023 and will commence drilling in early January 2024.